Anticoagulant Therapy
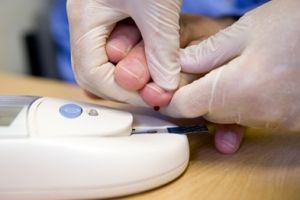
Anticoagulants are a class of drugs that work to prevent the coagulation (clotting) of blood.
Anticoagulants reduce blood clotting which can help prevent deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.
Therapeutic uses of anticoagulants include atrial fibrillation, pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, venous thromboembolism, congestive heart failure, stroke, myocardial infarction, and genetic or acquired hypercoagulability.
The decision to begin therapeutic anticoagulation often involves the use multiple bleeding risk predictable outcome tools clinicians use as non-invasive pre-test stratifications due to the potential for bleeds while on blood thinning agents
Click to learn more about the medications available.
